- +90 236 233 20 03
- info@metamold.com
- Customer Portal
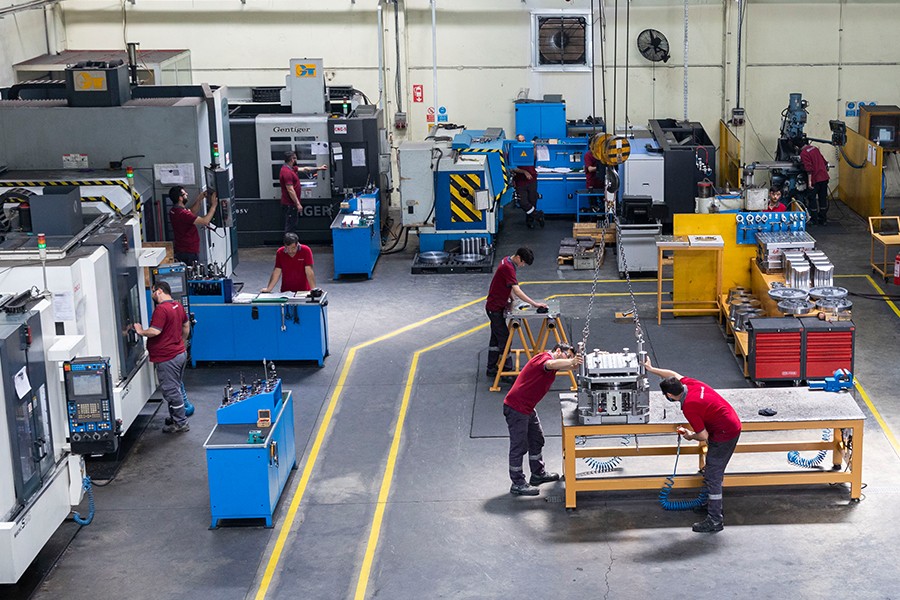

As one of the leading companies in the sector for High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) Molds, Metamold distinguishes itself through its high technology, experienced expert staff, and superior quality approach. Our commitment to quality is reflected in our production line, which is equipped with state-of-the-art CNC machines and CAD software. This enables us to produce highly precise and durable molds, even in the most complex projects.
The expert team at Metamold offers customer-oriented solutions with years of experience and knowledge. The molds we produce using high-quality and durable steel provide long-term high performance while offering a cost advantage. Our production processes are supported by internationally certified standards and are inspected at every stage through comprehensive testing and quality control procedures.
Our investments in R&D fuel our goal of continuous innovation and development, enhancing our production with the latest technologies. At Metamold, we take pride in being recognized in the industry for quality, reliability, and customer satisfaction.
High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) is a method where molten metal is injected into a mold under high pressure to shape the metal. This method, which uses lightweight metals like aluminum, magnesium, and zinc, enables the production of complex parts with thin wall thicknesses. The molds are typically made of steel and are designed to withstand repeated use. HPDC is preferred in production processes requiring high speed and precision.
Mold Design Stages:
Relationship Between Product Quality and Design:
The relationship between product quality and design is strong and plays an important role at every stage of the production process. A design with the correct geometry ensures defect-free casting and the production of products with accurate dimensions. This helps produce items within the desired tolerances. Surface quality contributes to the production of smooth and aesthetically pleasing parts, improving both the appearance and functionality of the final product. A flawless design minimizes casting defects such as gas voids and deformation, reducing losses during production.
Mechanical durability is particularly important in critical industries such as automotive, aerospace, and defense, and the correct design contributes to the longevity of parts. An efficient design accelerates the production process and lowers costs, creating a competitive advantage. Additionally, a long-lasting mold reduces maintenance costs, enhancing sustainability in the production process. Ultimately, proper design not only increases product quality but also optimizes production efficiency, offering significant advantages to companies.
High Pressure Die Casting Mold Production Processes
 Design and Planning
Design and Planning  Material Selection
Material Selection  CNC Machining
CNC Machining  Heat Treatment
Heat Treatment  Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)  Cooling Channels
Cooling Channels  Assembly and Fitting
Assembly and Fitting  Test and Quality Control
Test and Quality Control  Surface Treatments
Surface Treatments 
High Pressure Die Casting Molds offer many advantages in terms of fast production and high efficiency. The rapid solidification of the metal ensures short production cycles, speeding up the manufacturing process. The effective use of cooling systems allows production to continue uninterrupted. Additionally, high automation integration reduces dependence on human labor, lowering production costs. The ability to produce at high volumes reduces per-unit costs, making it a significant advantage in industries like automotive and electronics.
High Pressure Die Casting Molds stand out for their high precision and durability. This method enables the production of thin and complex parts with great accuracy, making it ideal for precision manufacturing processes. Moreover, the flawless surface quality achieved reduces the need for secondary processing. Parts produced with lightweight and durable metals are resistant to harsh working conditions, while the molds themselves are resistant to wear and have a long lifespan. The HPDC method provides both fast and efficient production and the creation of high-quality, durable parts, making it an excellent choice for large-scale production.
Mold Preparation and Casting Stages:
Quality Control and Final Inspections:
Ways to Extend Mold Lifespan:

The Importance of Regular Maintenance:

What is High Pressure Die Casting Mold?
A High Pressure Die Casting Mold (HPDC) is a mold used in a casting method where molten metal is injected into the mold under high pressure to produce metal parts. These molds are commonly used for lightweight metals in the production of complex and precise parts.
What metals are cast with High Pressure Die Casting Mold?
The most commonly used metals are aluminum, magnesium, and zinc alloys. These metals are preferred for their lightweight, durability, and aesthetic properties.
Where is High Pressure Die Casting Mold used?
HPDC molds are used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, household appliances, telecommunications, and energy. This method is used to produce engine blocks, transmission housings, wheels, phone cases, and electric motor components.
What are the advantages of High Pressure Die Casting Mold?
HPDC offers fast production cycles, high precision, durability, and surface quality. It also allows for economical production in large volumes and is effective in producing finely detailed, complex parts.
How precise can the parts produced with High Pressure Die Casting Mold be?
Parts produced by the HPDC method can be manufactured with high precision. Typically, parts can be produced within a tolerance range of ±0.1 mm, ensuring high accuracy even in thin-walled and complex geometries.
What is the lifespan of a mold?
The lifespan of a mold depends on the material used, casting frequency, and maintenance practices. Generally, a HPDC mold is designed to perform between 50,000 and 150,000 casting operations. Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of the mold.
What are the costs of molds?
The cost of High Pressure Die Casting Molds varies depending on the size, complexity, material, and the number of parts to be produced. Although the initial cost is high, it offers a cost advantage in large-volume productions.
What is the difference between HPDC and other casting methods?
HPDC involves injecting metal into the mold under high pressure, allowing for rapid production cycles and the production of precise parts. Other methods may operate at lower pressures and generally produce thicker parts. HPDC is advantageous for thin-walled and complex geometries.
How is mold maintenance carried out?
Mold maintenance involves regular cleaning, lubrication, and surface inspections. Keeping the cooling systems and channels inside the mold clean is also important. Mold release agents are applied after each casting cycle to extend the mold's lifespan.
How many parts can be produced with a High Pressure Die Casting Mold?
HPDC molds are ideal for large-scale production. Thousands, or even hundreds of thousands, of parts can be produced from a single mold. The mold material and the maintenance done to preserve quality increase this number.
What defects can occur during casting?
In high pressure casting, defects such as gas voids (porosity), shrinkage, cracks, or surface flaws can occur. These defects may arise from improper filling of the mold with casting liquid, uncontrolled cooling rates, or insufficient mold maintenance. With correct mold design and casting parameters, these defects are minimized.
What is the surface quality of HPDC parts?
Parts produced by the HPDC method generally have a very high surface quality. A smooth and aesthetic surface is achieved, allowing parts to be used without additional processing. Surface quality is especially critical in the production of wheels and electronic device cases.
Why are HPDC molds suitable for aluminum and zinc?
Lightweight metals like aluminum and zinc are easily shaped during casting, possess good fluidity, and provide high durability. These metals offer high strength and lightness, making them ideal for the HPDC method, particularly for thin-walled and complex geometries.
Is HPDC an environmentally friendly method?
HPDC is considered an environmentally friendly production method. Recyclable materials are used, and production is carried out without significant material waste. Furthermore, the high efficiency and fast production process save energy.
Can low-volume production be done with HPDC?
High pressure die casting is typically used for large-volume productions as mold production has a high initial cost. However, small-volume production can be done depending on the quality of the parts and the project requirements.