- +90 236 233 20 03
- info@metamold.com
- Customer Portal
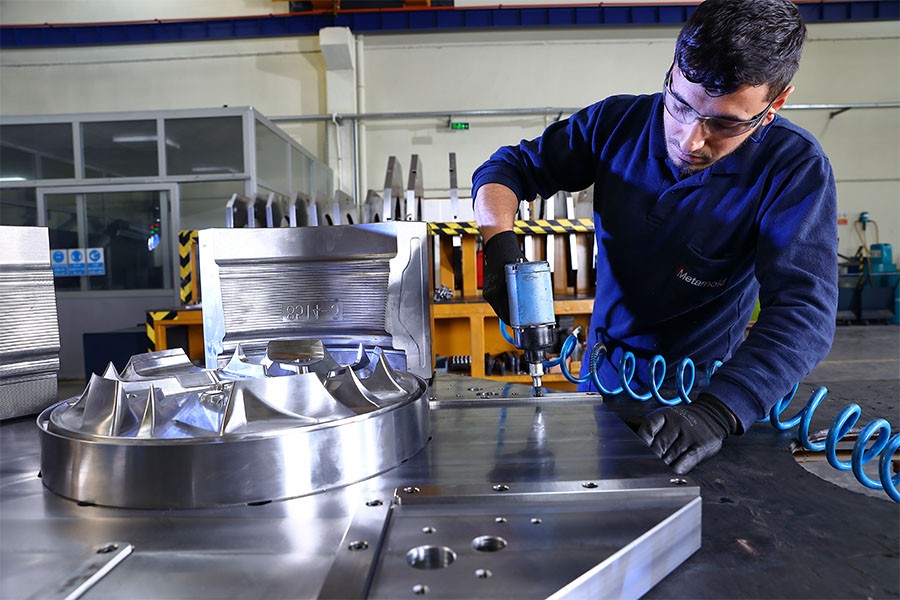

Aluminum wheel molds are an indispensable solution in the automotive industry due to their lightness, durability, and flexibility in aesthetic design. On our site, you can find comprehensive information on the production processes, materials used, casting technologies, and maintenance and repair of aluminum wheel molds. Discover the details of Low Pressure Die Casting (LPDC) and High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) technologies and the advantages aluminum offers compared to steel and other materials. All the technical information and innovative solutions needed for high-quality and long-lasting aluminum wheel production are provided on this page.
Aluminum wheel molds are essential tools used in the automotive industry for the production of wheels from aluminum alloys. The lightness and durability of aluminum contribute to enhancing vehicle performance through these molds. The production process requires high precision and, as a result, offers advantages in aesthetics, performance, and safety.
The design of aluminum wheel molds is a process that requires engineering expertise and attention. The design affects the shape, size, and aesthetic features of the wheel, while proper mold usage reduces costs and increases efficiency. The process includes need analysis, material selection, 3D modeling, cooling system design, flow channel planning, and assembly mechanisms. The design is tested through prototype production. Casting method, heat management, mold durability, production speed, and aesthetic details are also critical factors to consider.

The production of aluminum wheel molds is a complex and precise process, planned carefully to produce high-quality and durable wheels. The production stages include material selection, modeling, machining, surface treatments, and testing processes, each of which is of great importance.
1- Design and Engineering:
The production of aluminum wheel molds begins with the design phase using CAD software. At this stage, the shape, aesthetics, and performance criteria of the wheel are considered, and design details are determined according to the casting method (HPDC, LPDC).
2- Prototype Production:
After the design is completed, a prototype mold is produced to test and verify possible errors. The prototype is tested with a small production run and improved as necessary.
3- Material Selection:
Aluminum wheel molds are usually made from high-quality steel or cast iron. These materials ensure the durability, wear resistance, and longevity of the mold, with steel particularly resistant to deformation at high temperatures.
4- Machining (CNC Milling and Turning):
In the machining stage, a steel block is precisely milled, turned, and drilled according to the mold design using CNC machines, ensuring that every detail of the mold is correctly processed. This is one of the most important steps in mold production.
5- Cooling System Integration:
The cooling system ensures the heat in the mold is quickly dissipated, helping the aluminum solidify correctly. Properly placed cooling channels extend the mold’s life and reduce errors in wheel production.
6- Surface Treatments and Polishing:
After machining, the mold’s surface is made smooth and clean. Surface treatments and polishing ensure the wheels are produced with a high-quality surface. Special coatings may also be applied to prevent wear.
7- Assembly and Mold Trials:
In the assembly phase, the mold parts are assembled and prepared for the casting process. The mold is then tested for proper functionality, cooling system efficiency, and casting errors.
8- Mold Test and Approval Process:
Once mold production is complete, initial production trials are conducted. These tests measure the mold’s precision, durability, and surface quality of the wheel. Possible problems are identified, and corrections are made.
The prices of aluminum wheel molds vary depending on several factors. The main factors affecting prices include mold design and complexity, material quality, production method (HPDC, LPDC), workmanship and technical expertise, mold size and weight, production quantity, maintenance and repair costs, and market demand and competition. More complex designs, higher quality materials, and advanced production techniques increase prices, while mass production and long-lasting molds can optimize costs. Market demand and competition also directly influence prices.

The market prices for aluminum wheel molds vary depending on size, material quality, and design complexity. Small and medium-sized wheel molds are generally priced between $15,000 and $50,000, while large commercial vehicle wheel molds range from $50,000 to $150,000. Custom design and high-performance wheel molds can range from $100,000 to $250,000 due to more complex engineering and craftsmanship requirements.
Aluminum wheel molds offer advantages in the automotive industry such as lightness, durability, aesthetics, heat distribution, structural flexibility, low production costs, and improved performance. Aluminum is lighter and more corrosion-resistant than steel, offering modern designs and customizable aesthetics. Additionally, it distributes heat better, improving braking performance, providing flexibility against impact, and saving energy in the production process. These features enhance vehicle fuel efficiency, driving quality, and maneuverability.
| Feature | Aluminum Wheel Molds | Steel Wheel Molds | Plastic Wheel Molds |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Light | Heavy | Very Light |
| Durability | Medium - High | High | Low |
| Impact Resistance | Medium | High | Low |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Low | Very High |
| Heat Distribution | High | Medium | Low |
| Aesthetic Variety | Very High | Low | Medium |
| Cost | Medium - High | Low | Low |
| Application Areas | Broad | Broad | Limited |
The durability and performance of aluminum wheel molds depend on the quality of the materials used. Aluminum alloys are preferred in the automotive industry due to their lightness, strength, and aesthetic appearance. These alloys enhance the properties of pure aluminum, offering advantages such as lightness, corrosion resistance, high strength, and workability in wheel production.
 A356 Aluminum Alloy
A356 Aluminum Alloy 6061 Aluminum Alloy
6061 Aluminum Alloy AlSi7Mg Aluminum Alloy
AlSi7Mg Aluminum Alloy 7075 Aluminum Alloy
7075 Aluminum Alloy 5083 Aluminum Alloy
5083 Aluminum AlloyRegular maintenance and repair are essential for the efficient use of aluminum wheel molds. Since molds are exposed to high temperatures and pressure, they may wear out or deform over time. Regular maintenance extends the mold’s life, reduces production errors, and lowers costs. Repair processes make damaged molds reusable, reducing costs and extending their lifespan.
Mold Cleaning:
Mold cleaning should be performed after production cycles are completed or a specific production volume is reached. Aluminum particles and dirt that accumulate during production can reduce the mold’s performance. Methods such as air pressure, brushing, or chemical cleaning ensure sensitive and effective cleaning without damaging the mold’s surface.
Cooling Channels Maintenance:
Cooling channels ensure that heat is properly distributed during production. Blockages or damages can result in improper cooling of the aluminum and a decline in quality. These channels should be regularly inspected, and blockages should be cleaned with suitable equipment and solvents.
Lubrication and Use of Lubricants:
Regular lubrication of the mold’s moving parts prevents wear and extends the mold’s life, reducing friction. Proper lubricants prevent the metal from sticking to the mold. This process should be repeated periodically depending on production frequency.
Regular Inspections and Examination:
Molds may develop wear or micro-cracks during production, so regular inspections are crucial. Visible damage should be checked, and detailed areas should be examined under a microscope. If wear or cracks are detected, repairs should be made.
Wear and Surface Repair:
Molds that are in constant contact with aluminum during production may experience wear, especially in areas exposed to high temperatures. Wear is addressed with grinding or polishing processes, restoring the mold to its original form. If necessary, surface coatings are renewed.
Crack and Damage Repair:
Molds may develop cracks due to continuous thermal expansion and impacts, which can reduce wheel production quality. Cracks are filled with specialized welding techniques, and the mold is restored to its original condition through surface processing methods.
Cooling Channel Repair:
If cooling channels are blocked or damaged, improper heat distribution can affect production quality. Blocked channels are cleaned with special tools, damaged channels are repaired, and new channels are added as needed to improve the system.
Surface Coating Renewal:
Surface coatings enhance the mold’s wear resistance and prevent aluminum from sticking to the mold. However, these coatings may wear out over time. The coatings are stripped, the surface is cleaned, and it is recoated with the appropriate material. This process is carried out according to the mold’s production process and casting conditions.
The main casting technologies used in aluminum wheel production are Low Pressure Die Casting (LPDC) and High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) methods. LPDC is a method in which molten aluminum is injected into the mold under low pressure. This process provides controlled filling and leads to fewer air voids within the wheel structure. HPDC occurs by injecting molten aluminum into the mold rapidly under high pressure, making it suitable for mass production and enabling the production of a large number of wheels in a short time.
Low Pressure Die Casting (LPDC) is a casting method where molten aluminum is injected into the mold under low pressure. This process results in fewer air voids and defects in the wheel’s internal structure. LPDC’s advantages include high structural durability, a quality surface, and detailed aesthetics. However, the production process is slower, making it ideal for producing high-quality and durable wheels, though less suitable for mass production. It is commonly used for commercial vehicles, sports cars, and custom-designed wheels.
When Should LPDC Be Preferred?
High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) is a casting method in which molten aluminum is injected into the mold at high pressure. HPDC’s advantages include fast production, efficiency, and cost benefits. It is ideal for mass production and is commonly used in the large-scale production of passenger vehicle wheels. However, due to the rapid production, there can be micro voids and defects within the internal structure, limiting durability. HPDC is typically preferred for cost-driven projects and areas requiring quick production.
When Should HPDC Be Preferred?
| Feature | LPDC (Low Pressure Die Casting) | HPDC (High Pressure Die Casting) |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Level | Low (0.5-1 bar) | High (1000 bar and above) |
| Production Speed | Slower, less efficient | Very fast and efficient |
| Surface Quality | High, finely detailed | Good, but may have some internal defects |
| Durability | High structural durability | Medium durability |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
| Applications | Commercial vehicles, sports cars | Passenger vehicles, mass production |
| Volume Production | Less suitable | Ideal for high-volume production |
What is an aluminum wheel mold?
An aluminum wheel mold is a mold used in the casting process of wheels made from aluminum alloys. These molds determine the design, dimensions, and surface quality of the wheel. Through the mold, wheels are produced by giving liquid aluminum a specific shape while it’s in its molten state.
What materials are used to make aluminum wheel molds?
Aluminum wheel molds are generally made from high-quality steel or cast iron. These materials are chosen to ensure the mold’s durability and longevity. The materials used in mold production are selected to withstand the high temperatures and pressure during the production process.
What casting methods are used to produce aluminum wheel molds?
The most common casting methods used for aluminum wheel molds are Low Pressure Die Casting (LPDC) and High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC). LPDC offers higher durability and aesthetic quality, while HPDC is preferred for mass production and fast production processes.
How long do aluminum wheel molds last?
The lifespan of aluminum wheel molds depends on production frequency, material quality, and regular maintenance processes. Well-maintained molds made from high-quality materials can be used for the production of thousands of wheels.
What are the advantages of aluminum wheel molds?
Compared to steel and other materials, aluminum wheel molds offer advantages such as lightness, high strength, corrosion resistance, and a wide range of aesthetic design options. Additionally, aluminum conducts heat well, helping to distribute heat during braking, which improves braking performance.
How is the maintenance of aluminum wheel molds performed?
The maintenance of aluminum wheel molds includes regular cleaning, inspection of cooling channels, lubrication, and the repair of surface wear. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the long life of the molds.
What is the cost of aluminum wheel molds?
The cost of aluminum wheel molds varies depending on the size, complexity, and materials used in the mold. Small and medium-sized wheel molds can range from $15,000 to $50,000, while molds for commercial vehicles or custom designs can range from $50,000 to $150,000.
What alloys are used in aluminum wheel molds?
The most commonly used alloys in aluminum wheel production are A356, 6061, and AlSi7Mg, which are high-strength and high-casting-quality aluminum alloys. These alloys are preferred to increase the lightness and durability of the wheel.
Which industries use aluminum wheel molds?
Aluminum wheel molds are widely used in the automotive industry for passenger vehicles, commercial vehicles, sports cars, electric vehicles, and heavy-duty trucks. They are also used in agriculture machinery, defense industries, and some motorcycles and bicycles.
What are the differences between aluminum wheel molds and steel wheel molds?
Aluminum wheel molds are lighter and offer more aesthetic design options compared to steel molds. They are also more resistant to corrosion. However, steel wheels may be cheaper and provide higher impact resistance. Aluminum wheels, on the other hand, offer better heat distribution and performance.
Which production technology should be preferred for aluminum wheel molds?
Different casting technologies can be preferred depending on production volume, cost, and quality requirements. Low Pressure Die Casting (LPDC) is preferred for wheels requiring higher strength and aesthetic quality, while High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) is suitable for mass production and cost-effective large-scale manufacturing.
Are aluminum wheel molds recyclable?
Yes, aluminum wheel molds and aluminum wheels are recyclable. Aluminum is a material that can be reused without harming the environment, offering an eco-friendly solution.