- +90 236 233 20 03
- info@metamold.com
- Customer Portal
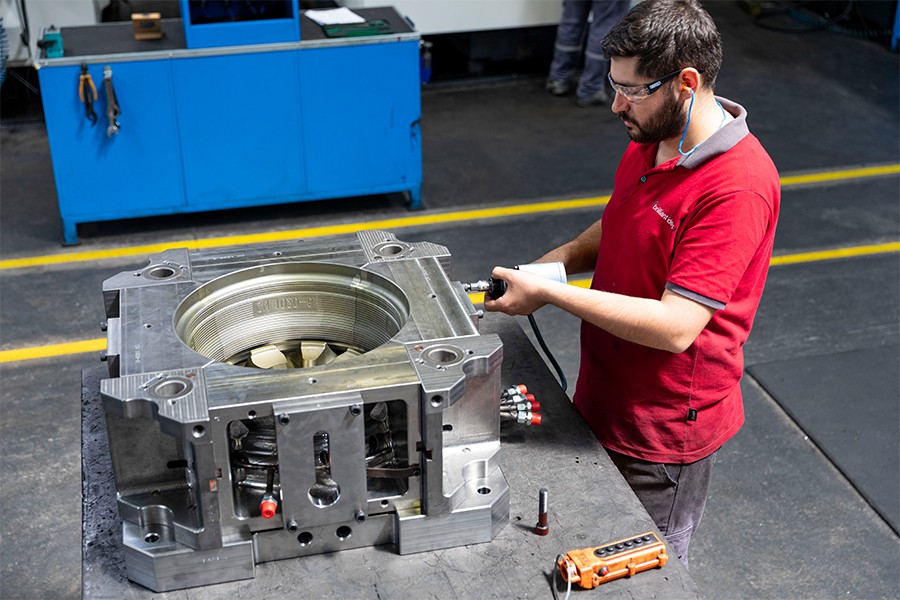

As Metamold, our steel wheel molds are specially designed molds produced to industrial standards, providing high strength and durability. Our products are designed with performance and safety in mind, particularly for the automotive industry, offering long-lasting use. Our steel wheel molds, produced using modern manufacturing techniques and precise engineering processes, offer superior resistance to high pressure, heat, and impacts. With our solutions focused on high-quality production, efficiency, and customer satisfaction, we make a difference in wheel manufacturing.
Steel wheel molds are special molds that allow the production of steel wheels through casting or shaping methods. Known for their durability, high load-bearing capacity, and longevity, steel wheels are used in areas such as automotive, commercial vehicles, and agricultural machinery. The mold production process involves stages like CAD design, CNC machining, heat treatment, surface coating, and polishing. The manufactured wheels undergo dimensional control, durability, and surface tests. The advantages of steel wheel molds include durability, high production capacity, and cost-efficiency.
Steel wheel molds play a critical role in the production of wheels in the automotive and heavy industry sectors. These molds, which stand out with factors such as durability, precision, and cost-effectiveness, offer high strength and long life. Steel molds provide efficiency in production processes, offering many advantages compared to molds made of other materials. This article details the durability and production advantages of steel wheel molds.
Durability Advantages
Steel wheel molds offer long life and reliability as they are resistant to wear, high temperatures, and impacts. Due to their high strength, they can maintain their shape under significant pressure. Their heat resistance ensures structural integrity during the high temperatures of wheel production. Thanks to their wear resistance, they can last a long time even with continuous use. As they are impact-resistant, they can be used without deformation during production despite mechanical stresses.
Production Advantages
Steel wheel molds offer significant advantages in production processes. Their long service life enables large-scale production without frequent replacements. High mass production capacities increase efficiency and reduce cost per unit. Their durability leads to low production costs. Precision manufacturing ensures that wheels meet high-quality standards and minimizes production defects. Moreover, steel material offers flexibility for complex and detailed designs.
Ease of Maintenance and Repair
Although steel wheel molds are durable, they may require maintenance and repair after extended use. Their easy repairability allows for issues to be resolved with welding and re-machining in case of damage, extending the mold's life. Heat treatment and surface coatings improve the durability and wear resistance of the molds, making the maintenance process more efficient.
Environmental Sustainability
Steel is a recyclable material, making it advantageous in terms of environmental sustainability. Steel wheel molds can be recycled after their service life, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, recycled steel can be used in the production of new molds.
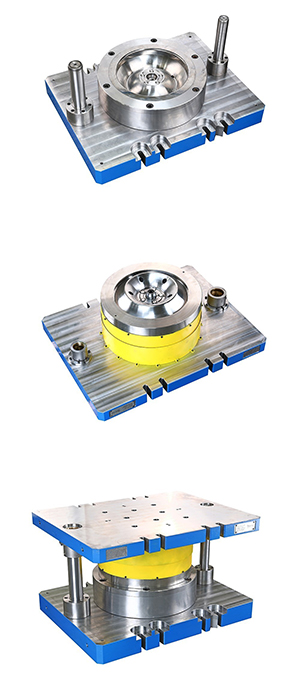
Steel wheel mold prices vary depending on factors such as design, production processes, and materials used. Engineering knowledge, advanced technology, and craftsmanship are also important variables that affect the cost. This article examines the main factors determining the prices of steel wheel molds.
Design Complexity: One of the most significant factors affecting the prices of steel wheel molds is design complexity. Geometrical structures and details, especially complex and custom designs, increase the cost. Tolerance accuracy, which is necessary when the wheel requires high precision, demands more complex production processes and thus increases the cost.
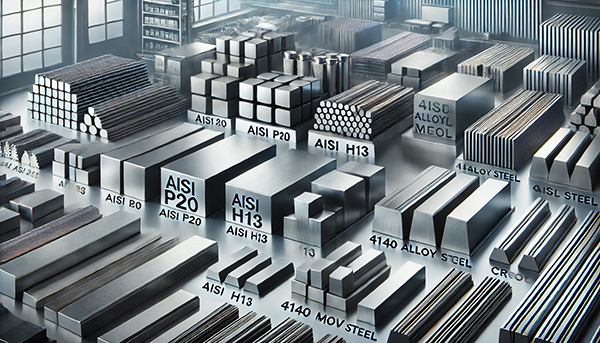
Type of Material Used: The type of steel used affects the prices of steel wheel molds. Steel quality, especially high-strength alloys (AISI P20, H13), increases the cost. Processes such as heat treatment and coating extend the life of the mold by enhancing its durability, but these also increase the cost.
Production Volume and Scale: The prices of steel wheel molds vary according to the scale of production. Low-volume productions have a higher cost per unit because the mold costs are distributed over fewer products. Mass production, on the other hand, provides a cost advantage as more products are produced, reducing the cost per unit.
Labor and Technology Use: Labor and technology use in mold production affect the costs. CNC machining, which ensures high precision and quality, increases costs. Manual labor, assembly, maintenance, and surface processes are other factors that increase costs. The quality of workmanship directly impacts the final price.
Mold Durability and Life: The durability and life of steel wheel molds are significant factors affecting costs. Long-lasting molds offer a high initial investment cost but require less maintenance and replacement in the long run, providing a cost advantage. High-quality materials and well-designed molds, which require low maintenance and repair, reduce costs in the long term.
Heat Treatment and Coating Techniques: Heat treatment and coating techniques affect the cost by enhancing the durability of steel wheel molds. Heat treatment makes the molds harder and more durable, initially increasing the cost but providing advantages in the long run. Coating (such as nitriding, chrome plating) increases wear resistance and extends the mold's life, increasing the initial cost but reducing costs in the long term.
Mold Design Time and Engineering Work: Mold design time and engineering work affect the cost of steel wheel molds. The use of CAD and CAE software optimizes the production process and reduces errors, but these processes also increase the cost. Prototype production and testing, while initially raising the cost, improve the mold's performance, resulting in long-term savings.
Production Location and Shipping Costs: Production location and shipping costs affect the price of steel wheel molds. The production region creates a price difference based on labor and material costs; production in low labor-cost regions can reduce costs. Shipping and customs fees, especially in international productions, are significant factors that increase costs due to the size and weight of the molds.
Steel wheel molds play a critical role in the production of wheels in the automotive industry. The design and manufacturing techniques of these molds affect the quality, durability, and cost of the wheels. The design process consists of stages requiring high precision and engineering knowledge. The technologies used in the production of wheel molds play an essential role in increasing production quality. This article elaborates on the design and production processes of steel wheel molds.


The materials used in the production of steel wheel molds are critical in terms of the molds' durability, performance, and life. Material selection is based on the mold's exposure to temperature, pressure, and wear during the production cycle, ensuring the mold's strength and efficiency.


Regular Cleaning
Regular cleaning of the molds prevents wear and damage, preserving the quality of the wheels. Surface cleaning removes accumulated metal debris, oil, and dust during production. Oil and residue cleaning preserves surface smoothness, preventing quality issues. Appropriate cleaning materials should be non-abrasive and not harmful to steel.
Mold Surface Protection and Coating
Protecting the mold surface extends its life and improves production quality by preventing wear. Protective coating (chrome or nitriding) shields the surface against wear and corrosion. Polishing removes surface deformations, maintaining smoothness and ensuring the mold works efficiently and produces high-quality wheels.
Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening
Regular heat treatment and surface hardening should be applied to enhance the durability of steel wheel molds. Heat treatment restores the mold's hardness, improving resistance to high temperature and pressure. Surface hardening (e.g., nitriding) makes the outer surface harder and more resistant to wear.
Regular Inspection and Control
Regular inspection of molds allows for the early detection of issues, preventing major malfunctions. Dimensional control checks if the mold complies with design dimensions, while surface inspection detects cracks and wear, allowing for early repairs and preventing significant damage.
Repair and Revision
When molds wear out after long-term use, regular repair and revision procedures extend the mold's life. Crack repair can be done with welding when detected early, preventing significant damage. Wear removal processes correct surface wear through polishing or coating. Revision updates the mold design to adapt to modern production technologies, increasing production quality.
Lubrication and Friction Reduction
Lubrication and friction reduction prevent wear and deformation of molds, extending their life. The correct choice of lubricants should be those that do not harm the mold's surface and can withstand high temperatures. Regular lubrication during production reduces friction in each cycle, ensuring efficient and long-lasting mold operation.
Mold Storage
Proper storage of molds prevents oxidation and corrosion. Protecting from moisture is achieved by keeping the molds in a dry and cool place. The use of protective sprays and coatings prevents corrosion and surface damage during the unused period, extending the life of the molds.
Operator Training
Operator training is critical for the proper use and maintenance of molds. Correct usage training teaches operators how to use, lubricate, and clean the molds, preventing misuse. Maintenance training ensures operators are knowledgeable about regular cleaning and lubrication procedures, extending the life of the molds.
| Feature | Steel Wheel Mold | Aluminum Wheel Mold |
|---|---|---|
| Material Durability | High strength, resistant to wear and impact | Less durable, sensitive to impacts |
| Heat Resistance | Durable under high temperatures | Resistant to lower temperatures, risk of deformation at high temperatures |
| Lightweight | Heavy | Light, easy to handle and process |
| Corrosion Resistance | Lower corrosion resistance in steel | Naturally corrosion-resistant |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Long-Term Cost | Lower, longer-lasting | Higher, may need to be replaced more frequently |
| Production Time | Longer, more difficult to process | Shorter, lighter and easier to process |
| Durability and Life | Durable and long-lasting | Shorter lifespan |
| Application Area | Heavy commercial vehicles and high-volume production processes | Cars and light commercial vehicles, low-volume productions |
What is a steel wheel mold?
A steel wheel mold is a mold used in the production of wheels for vehicles. Due to its durable and strong structure, it is often preferred for the production of wheels for heavy-duty vehicles and high-performance cars.
What materials are steel wheel molds made of?
Steel wheel molds are made of high-strength steel. Steel is long-lasting and reliable in wheel production processes, as it is resistant to heat and pressure.
Which vehicles are steel wheel molds suitable for?
Steel wheel molds are particularly suitable for heavy vehicles, commercial vehicles, trucks, and off-road vehicles. They are also preferred for performance cars because steel wheels provide strength and durability.
What are the differences between steel and aluminum wheel molds?
Steel wheel molds are heavier and more durable compared to aluminum wheel molds. Aluminum wheels offer advantages in terms of being lightweight and aesthetically appealing, while steel wheels are generally more economical and durable, making them ideal for challenging road conditions.
How long do steel wheel molds last?
The lifespan of steel wheel molds depends on the quality of the material and maintenance. Regular maintenance and cleaning help extend the life of the molds for many years.
What is the production process for steel wheel molds?
The production process of steel wheel molds typically involves hot casting. Metal is poured into the mold at high temperatures and shaped as it cools. The precision of the molds determines the dimensional and shape accuracy of the wheels produced.
What is the cost of steel wheel molds?
The cost of steel wheel molds varies depending on the size, design, and production technology of the mold. Generally, they are more affordable compared to aluminum molds.
What are the advantages of steel wheel molds?
Durability: Steel material is resistant to challenging road conditions and impacts. Economy: Steel wheel molds are generally more cost-effective. Reliability: Especially for vehicles carrying heavy loads, steel wheels provide more safety.
Are there any disadvantages of steel wheel molds?
The disadvantages of steel wheel molds include their weight and lower preference compared to aluminum wheels in terms of aesthetics. Additionally, due to the risk of rust, regular maintenance may be required.
What kind of maintenance do steel wheel molds require?
Regular cleaning and rust protection are necessary for the molds. Additionally, removing oil and other chemicals used in the wheel production process from the molds extends the life of the mold and enhances the quality of the wheels.